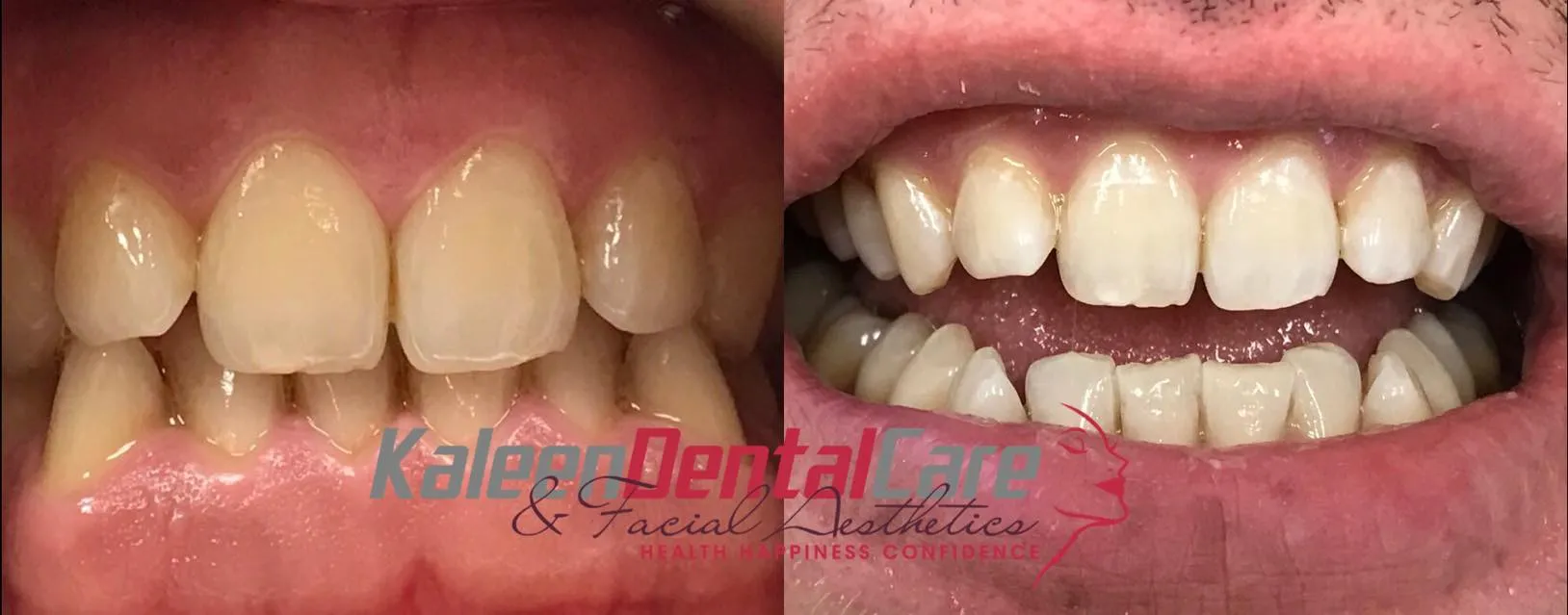
What is Laser Teeth Whitening?
Laser teeth whitening, also known as light-activated teeth whitening, is a cosmetic dental procedure designed to brighten and lighten the color of your teeth. This method uses a concentrated beam of light, often a laser, to accelerate the bleaching process of a whitening agent applied to the teeth. The procedure has gained popularity for its ability to deliver quick and noticeable results, making it a sought-after treatment for those looking to enhance their smile. Unlike at-home whitening kits, laser teeth whitening is typically performed by a dental professional, ensuring a controlled and supervised environment. This professional setting allows for the use of stronger whitening agents and the precise application of the laser to maximize effectiveness and minimize potential side effects. Before undergoing the procedure, your dentist will assess your oral health to determine if you are a suitable candidate.
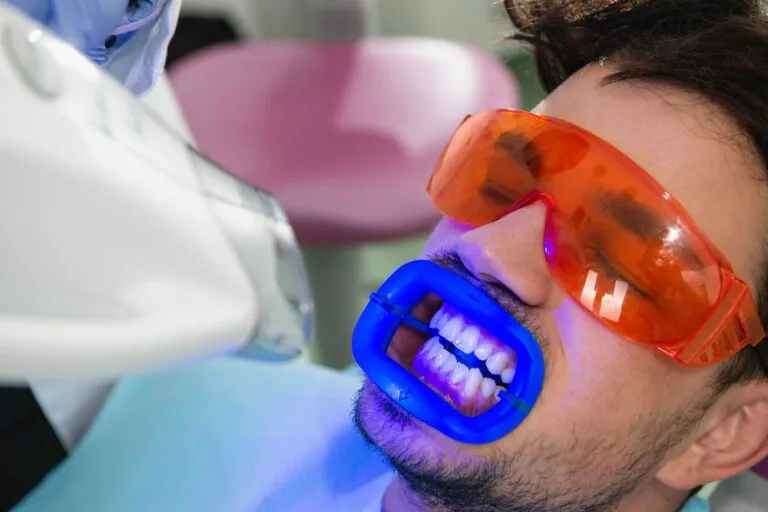
The Procedure of Laser Teeth Whitening
The laser teeth whitening procedure typically involves a few key steps. First, the dentist will clean your teeth to remove any plaque or debris that could interfere with the whitening process. Next, a protective barrier is placed over your gums to shield them from the strong bleaching agent and the laser light. This step is critical in preventing gum irritation. The whitening agent, usually a hydrogen peroxide-based solution, is then applied to the surface of your teeth. The dentist will use a laser to activate the whitening agent, which helps to break down the stains and discoloration on your teeth. The laser light itself doesn’t whiten the teeth, but it enhances the effect of the bleaching agent. The laser is directed at the teeth for a specific amount of time, and the process might be repeated several times during a single session to achieve the desired level of whitening. After the procedure, the dentist will remove the whitening agent and protective barriers, providing you with aftercare instructions.
Laser Teeth Whitening Fact 1 Sensitivity
One of the most common side effects of laser teeth whitening is increased tooth sensitivity. Many patients experience a temporary increase in sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks. This sensitivity occurs because the whitening agents can penetrate the enamel and reach the dentin layer of the tooth, which contains nerve endings. The laser light itself does not cause sensitivity, but it accelerates the whitening process and may exacerbate the sensitivity caused by the whitening agent. The intensity of sensitivity can vary from mild discomfort to more significant pain, depending on individual factors like the thickness of the enamel and the overall health of the teeth. This sensitivity typically subsides within a few days to a couple of weeks after the procedure. It is crucial to be prepared for this potential side effect and to take measures to manage it effectively.
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity After Laser Whitening
Several factors contribute to tooth sensitivity after laser teeth whitening. As mentioned, the whitening agents used in the process can penetrate the enamel and dentin, irritating the nerves. The concentration of the whitening agent is also a significant factor; stronger solutions can lead to more sensitivity. Individuals with pre-existing dental conditions, such as micro-cracks in the enamel, thinner enamel, or receding gums, may be more prone to experiencing sensitivity. Moreover, the use of the laser itself, by enhancing the whitening process, can amplify the sensitivity. The process opens up the pores of the enamel, allowing the whitening agent to reach the inner layers of the teeth more effectively. The temporary dehydration of the teeth during the procedure can also play a role. Understanding these causes can help you anticipate and manage the sensitivity more effectively.
How to Manage Sensitivity After Laser Whitening
Fortunately, there are several strategies to manage tooth sensitivity after laser teeth whitening. The dentist may recommend using a toothpaste specifically designed for sensitive teeth, which contains ingredients like potassium nitrate to help block the nerve signals that cause sensitivity. Avoiding extremely hot or cold foods and drinks for a few days after the procedure can also help to minimize discomfort. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, can be taken to alleviate any pain. In some cases, the dentist might apply fluoride varnish to the teeth to strengthen the enamel and reduce sensitivity. Staying hydrated and maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing and flossing, are also crucial during the recovery period. If sensitivity persists or becomes severe, consult your dentist, as additional treatments may be necessary.
Laser Teeth Whitening Fact 2 Gum Irritation
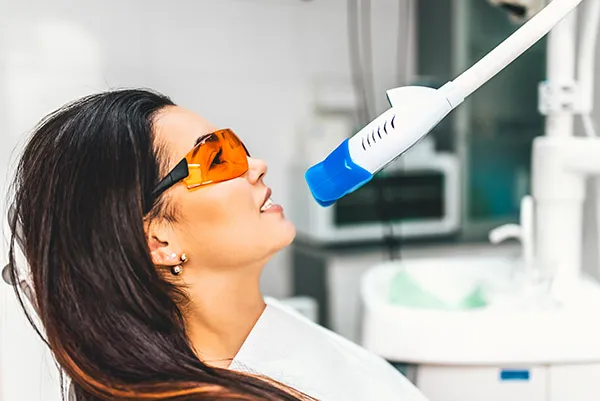

Gum irritation is another potential side effect of laser teeth whitening. This happens because the gums are sensitive tissues, and they can be affected by the whitening agents or the laser light if not adequately protected during the procedure. The irritation can manifest as redness, swelling, and tenderness in the gums. In some cases, the gums might feel sore or even bleed slightly. The severity of gum irritation can vary depending on how well the protective measures were applied and the individual’s sensitivity. While gum irritation is usually temporary, it can be uncomfortable. Proper precautions and aftercare are critical to minimize and manage this side effect.
Understanding Gum Irritation After Laser Whitening
The primary cause of gum irritation is exposure to the whitening agent. Although dentists take precautions, some of the bleaching solution might come into contact with the gums. The laser light itself can also cause irritation if it is not precisely targeted at the teeth. Additionally, certain individuals might have more sensitive gum tissues, making them more susceptible to irritation. The strength of the whitening agent used can also influence the level of irritation. The longer the gums are exposed to these irritants, the more pronounced the inflammation may become. Proper technique and the use of protective barriers are key to minimizing gum irritation.
Preventing Gum Irritation During the Procedure
Dentists take several steps to prevent gum irritation during laser teeth whitening. A protective barrier, such as a dental dam or a specialized gel, is applied to the gums to shield them from the whitening agent and the laser light. This barrier ensures that the whitening agent only contacts the teeth and prevents it from reaching the sensitive gum tissues. Careful application of the whitening agent is also essential. The dentist should apply the solution precisely to the teeth and avoid any contact with the gums. The laser is aimed with precision to target only the teeth, minimizing any potential exposure of the surrounding tissues. Regular monitoring during the procedure is also crucial, allowing the dentist to adjust the process if any signs of irritation appear. Patients should also communicate any discomfort or unusual sensations to their dentist immediately.
Laser Teeth Whitening Fact 3 Tooth Discomfort

In addition to sensitivity, some individuals experience tooth discomfort after laser teeth whitening. This discomfort can range from a mild ache to more noticeable pain. The pain is usually temporary and subsides within a few days, but it can be bothersome. This discomfort is often related to the inflammatory response of the tooth, as the bleaching agents and the laser affect the inner layers of the tooth. The intensity of the discomfort varies from person to person and depends on factors such as tooth sensitivity, the concentration of the whitening agent, and the individual’s pain tolerance. Proper aftercare can help to manage and alleviate any discomfort.
Causes of Tooth Discomfort Post Laser Whitening
The causes of tooth discomfort after laser teeth whitening are closely related to the mechanisms that lead to sensitivity. The whitening agents can irritate the nerves within the teeth, causing discomfort. The laser light, while not directly causing pain, can enhance the effects of the whitening agent and potentially increase discomfort. Microscopic changes in the enamel structure during the whitening process might also contribute to the pain. Any pre-existing dental issues, such as tiny cracks in the teeth, can also be a factor, as they can allow the whitening agents to penetrate more deeply. The level of dehydration of the teeth during the procedure can also cause discomfort. Understanding these underlying causes can help to manage the discomfort effectively.
How Long Does Tooth Discomfort Last?
The duration of tooth discomfort after laser teeth whitening varies from person to person. In most cases, the discomfort lasts for a few days to a week. However, some individuals may experience it for up to two weeks. If the discomfort is mild, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can provide relief. For more severe cases, the dentist may recommend stronger pain medications. The discomfort typically subsides as the teeth adjust to the procedure and the sensitivity decreases. If the pain persists or worsens, consult your dentist to rule out any other underlying issues and receive appropriate treatment. Following your dentist’s aftercare instructions is essential to speed up recovery.
Laser Teeth Whitening Fact 4 Uneven Whitening
Uneven whitening is a potential side effect where the teeth do not whiten uniformly across the surface. Some teeth might whiten more than others, or certain areas of a tooth might not whiten as much as others. This result can be frustrating for individuals seeking a brighter smile. Uneven whitening is typically more noticeable on teeth with pre-existing fillings, crowns, or other dental work because the whitening agents only affect the natural tooth structure. The degree of unevenness can vary. Understanding the causes of uneven whitening can help to manage expectations and explore strategies to minimize this effect.
Why Uneven Whitening Occurs
Several factors can contribute to uneven whitening. The natural variation in the enamel thickness and composition of the teeth can cause some teeth to whiten more easily than others. Teeth with different levels of staining or discoloration will also respond differently to the whitening agent. Existing dental work, such as fillings, crowns, and veneers, will not whiten with the procedure. These materials are designed to match the original tooth color and are resistant to the bleaching agents. The location of the teeth in the mouth can also play a role; teeth at the front of the mouth might receive more exposure to the whitening agent and laser light than those at the back. Inconsistent application of the whitening agent can contribute to unevenness. Understanding these factors can help the dentist tailor the procedure to achieve a more uniform result.
Addressing Uneven Whitening
Several strategies can address uneven whitening. In some cases, a second whitening session can help to achieve a more uniform result. The dentist might adjust the application of the whitening agent and the laser intensity to target specific teeth or areas. For teeth with existing dental work, the dentist can discuss options such as replacing the restorations to match the newly whitened teeth. Using custom trays at home with a lower concentration whitening agent can also help to gradually even out the whitening effect. The dentist can also recommend touch-up treatments to maintain the results. For particularly stubborn areas of discoloration, other cosmetic procedures, such as veneers, may be considered to achieve the desired aesthetic outcome. It’s important to discuss the expectations and potential solutions with your dentist before the procedure.
Laser Teeth Whitening Fact 5 Enamel Damage
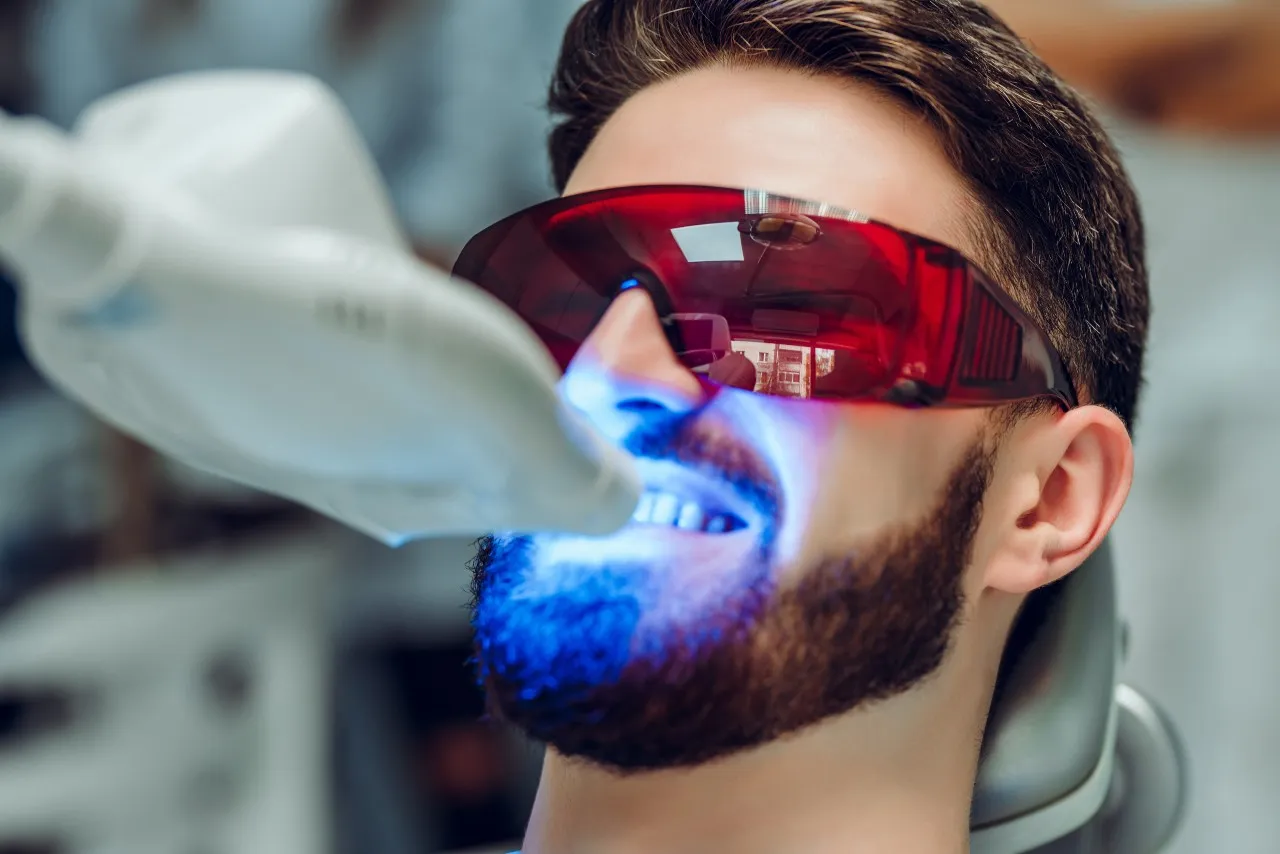

While rare, enamel damage is a potential side effect of laser teeth whitening. The whitening agents used in the procedure, usually containing hydrogen peroxide, can weaken the enamel if used excessively or improperly. The enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth, protecting the underlying dentin and nerves. Damage to the enamel can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, an increased risk of cavities, and a duller appearance. Although the risk of enamel damage is low when the procedure is performed by a qualified dental professional, it is essential to understand the potential risks and take steps to protect the enamel.
Understanding Enamel Damage and Laser Whitening
Enamel damage from laser teeth whitening is usually associated with the overuse of the whitening agent or the application of high concentrations of the agent. The bleaching agents can cause the enamel to lose some of its mineral content, making it more susceptible to erosion. The laser itself doesn’t directly damage the enamel, but its use can potentially exacerbate the effects of the whitening agents. Individuals with pre-existing enamel issues, such as erosion or cracks, are more at risk of enamel damage. The degree of enamel damage can vary. Preventive measures and following the dentist’s instructions are crucial to minimize the risk.
How to Protect Your Enamel During the Procedure
Several steps can be taken to protect your enamel during laser teeth whitening. Choosing a qualified and experienced dentist is critical. The dentist should use appropriate concentrations of the whitening agent and follow the recommended guidelines for the procedure. Protective measures, such as applying fluoride varnish after the procedure, can help to strengthen the enamel. Avoiding excessive whitening treatments and following the recommended frequency of treatments is also important. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, and using a soft-bristled toothbrush, helps to protect the enamel. Limiting the consumption of acidic foods and drinks, which can erode the enamel, can also help. Consulting with your dentist about the best methods to protect your enamel will ensure a successful and safe whitening experience.
Conclusion
Laser teeth whitening can be an effective way to achieve a brighter and more confident smile. However, it’s essential to be aware of the potential side effects, including sensitivity, gum irritation, tooth discomfort, uneven whitening, and, rarely, enamel damage. By understanding these potential risks and taking preventative measures, such as choosing a qualified dentist and following aftercare instructions, you can minimize the likelihood of these side effects and enjoy the benefits of a whiter smile. Remember to discuss your concerns and expectations with your dentist before undergoing the procedure, and always follow their recommendations for optimal results and dental health. Your dentist can assess your oral health, address any pre-existing conditions, and customize the treatment plan to suit your needs, ultimately ensuring a safe and successful laser teeth whitening experience. Good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups are essential to maintain a healthy and beautiful smile.