What Causes Sensitive Teeth After Whitening?
Teeth whitening is a popular cosmetic procedure, but it can sometimes lead to increased sensitivity. This sensitivity can range from mild discomfort to sharp, intense pain, making everyday activities like eating and drinking challenging. Understanding the causes of this sensitivity is crucial for effective treatment and management. Several factors contribute to this common side effect. Whitening treatments, whether performed at home or in a dental office, involve the use of bleaching agents that penetrate the enamel to remove stains. This process can temporarily alter the tooth structure, making it more susceptible to external stimuli like temperature changes and pressure. Moreover, individual differences in tooth structure and pre-existing conditions can also affect the degree of sensitivity experienced after whitening. Therefore, recognizing these factors can help in selecting appropriate treatment methods.
Tooth Whitening Products
The type of whitening product used significantly impacts the likelihood and severity of sensitivity. Over-the-counter products often contain lower concentrations of bleaching agents, such as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. While they may cause less sensitivity, the results might not be as dramatic. Professional whitening treatments, on the other hand, use higher concentrations of these agents, leading to more noticeable whitening but also a greater chance of sensitivity. These treatments are typically performed under the supervision of a dentist, who can monitor the process and provide guidance on managing potential discomfort. The formulation of the product also matters. Some products include desensitizing agents to minimize sensitivity, and these can be particularly beneficial for individuals prone to experiencing discomfort after whitening procedures. Therefore, considering the product type and its ingredients is essential when choosing a whitening treatment.
How Whitening Affects Teeth

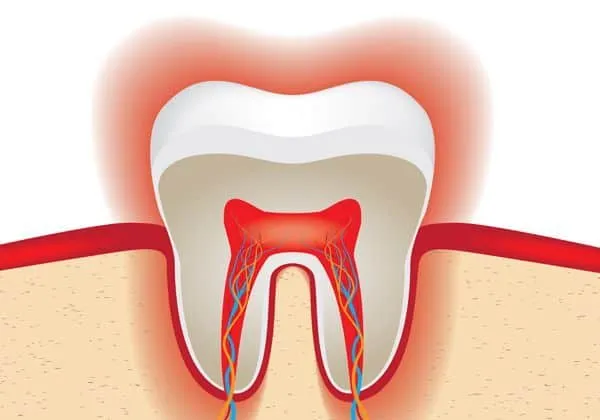
Whitening agents work by breaking down stain molecules within the enamel. This process can temporarily dehydrate the teeth, making the dentin tubules – tiny channels within the tooth that connect to the nerve – more exposed. The exposure of these tubules is a primary cause of sensitivity. When exposed, they can transmit sensations more easily to the nerves, leading to pain or discomfort. Additionally, the chemicals in whitening products can irritate the pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels. This irritation can also contribute to increased sensitivity. Understanding how these processes impact your teeth allows for a more informed approach to dealing with any sensitivity experienced. This also can help when planning the next whitening session.
Common Causes of Sensitivity
Sensitivity after whitening is typically caused by the bleaching agents affecting the enamel and dentin. The most common trigger is temperature, with hot and cold foods or drinks causing sharp, sudden pain. Pressure, such as from biting or brushing, can also exacerbate the discomfort. Furthermore, the extent of the sensitivity varies depending on the individual and the specific whitening method used. Some people may experience mild sensitivity for a few days, while others may have more severe pain that lasts for a longer period. The concentration of the bleaching agent, the duration of the treatment, and the presence of any pre-existing dental issues all play a role in how severe the sensitivity becomes. Therefore, being aware of these factors can help you prepare for and manage potential discomfort effectively.
Immediate Relief for Sensitive Teeth
If you experience sensitivity after whitening, several strategies can provide immediate relief. The first step is to avoid triggers such as hot or cold foods and beverages. Switching to lukewarm or room-temperature options can significantly reduce discomfort. Applying these strategies will help to make the treatment much more comfortable. In addition to avoiding triggers, you can explore other effective techniques. You can also consider some of the available solutions in order to get relief quickly and easily.
Use Desensitizing Toothpaste

Desensitizing toothpaste is specifically formulated to alleviate tooth sensitivity. These toothpastes typically contain ingredients like potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride, which work by blocking the dentin tubules, thereby reducing the transmission of sensations to the nerves. Using this type of toothpaste regularly can provide significant relief. For the best results, start using the toothpaste a couple of weeks before your whitening treatment. Continue using it during and after the whitening process. Make sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent further irritation of your gums. Using desensitizing toothpaste consistently can greatly improve your comfort and well-being.
Apply Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments can also help to strengthen the enamel and reduce sensitivity. Fluoride helps to remineralize the enamel, making the teeth more resistant to external stimuli. You can apply over-the-counter fluoride rinses, or, for more severe sensitivity, your dentist can provide professional fluoride treatments. These treatments usually involve the application of a high-concentration fluoride gel or varnish. They are designed to be applied in-office and can provide a more potent dose of fluoride to help alleviate sensitivity. Professional treatments can offer faster and more significant relief. Always consult your dentist about the best type of fluoride treatment for your situation, as they can offer personalized advice and recommendations.
Avoid Whitening for a While
If sensitivity persists or worsens, consider pausing your whitening treatments. Allow your teeth to recover and become less sensitive before resuming the process. This may involve stopping the use of whitening strips, gels, or professional treatments for a few weeks or even months. During this time, focus on using desensitizing toothpaste and avoiding triggers. This approach provides your teeth with the opportunity to recover naturally. Always be patient and allow your teeth to heal completely before reinitiating any whitening procedures. It’s essential to communicate any concerns with your dentist.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relief

For immediate pain relief, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be helpful. These medications can temporarily reduce the discomfort associated with tooth sensitivity. However, always follow the dosage instructions on the product label and be aware of any potential side effects. It’s best to use these pain relievers as a short-term solution, rather than a long-term fix. If the sensitivity is severe or persistent, consult your dentist to rule out any underlying dental issues. Using these simple methods can help to manage the symptoms, allowing you to continue your daily life with minimal discomfort.
Long-Term Solutions and Prevention
While immediate relief is crucial, adopting long-term strategies can help prevent and manage tooth sensitivity. This includes maintaining proper oral hygiene practices, making dietary adjustments, and scheduling regular dental check-ups. By focusing on preventative measures, you can minimize your risk of experiencing sensitivity and maintain a healthy, comfortable smile. Incorporating these steps into your daily routine will contribute to lasting oral health.
Proper Brushing Techniques
Proper brushing techniques are fundamental to preventing sensitivity and maintaining healthy teeth. Brush your teeth gently using a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating the gums and enamel. Apply minimal pressure while brushing, and use a circular or back-and-forth motion, rather than scrubbing harshly. Brushing too aggressively can wear away enamel and expose the dentin tubules, leading to increased sensitivity. Ensure you brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. The most common mistakes are the use of a hard-bristled toothbrush or an aggressive brushing technique. Always brush for at least two minutes, twice a day, and consider using an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor to help maintain the correct technique.
Choose the Right Toothbrush

Selecting the right toothbrush is vital for sensitive teeth. Opt for a soft-bristled toothbrush, as it is gentle on the enamel and gums. Hard bristles can cause abrasion, leading to enamel erosion and increased sensitivity. Look for toothbrushes with rounded or polished bristles to further protect your teeth. Consider an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor, as it can help you brush with the correct amount of pressure. Replace your toothbrush every three months or sooner if the bristles become frayed. Replacing your toothbrush frequently helps ensure its effectiveness.
Use a Gentle Approach
Adopt a gentle approach to brushing to prevent damaging your enamel and gums. Avoid using excessive force or scrubbing motions. Instead, use a circular or back-and-forth motion, ensuring you reach all surfaces of your teeth. Spend sufficient time on each tooth, ensuring thorough cleaning without causing irritation. If you have sensitive teeth, you might benefit from using a special technique to avoid aggravating the sensitivity. A gentle approach also means being mindful of your overall oral health. This will reduce the risk of developing sensitivity problems in the future. Be patient and consistent with your brushing technique.
Dietary Considerations
Dietary habits play a crucial role in managing tooth sensitivity. Certain foods and drinks can trigger or worsen sensitivity. Limiting the consumption of these items can help reduce discomfort and protect your teeth. By making conscious choices about what you eat and drink, you can significantly improve your oral health and comfort.
Limit Acidic Foods and Drinks
Acidic foods and drinks can erode enamel, making your teeth more sensitive. Minimize your intake of citrus fruits, tomatoes, pickles, and carbonated beverages. These items have high acid content that can weaken the enamel. When consuming acidic foods, rinse your mouth with water afterward to neutralize the acid and minimize the damage. Avoiding these types of foods and drinks can lessen your sensitivity symptoms. If you enjoy these foods, consume them in moderation and combine them with non-acidic foods to help mitigate the impact.
Hydration and Saliva Production
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for oral health and can also help manage sensitivity. Drinking plenty of water helps maintain saliva production, which naturally neutralizes acids in the mouth and remineralizes the enamel. Saliva acts as a protective barrier for your teeth, reducing the risk of sensitivity. Moreover, it also helps in washing away food particles and bacteria. If you struggle with dry mouth, consider chewing sugar-free gum or using saliva substitutes to stimulate saliva production. Ensure you are drinking enough water throughout the day. This also contributes to your overall health and well-being.
Professional Dental Care
Regular visits to your dentist are essential for managing and preventing tooth sensitivity. A dentist can diagnose the cause of the sensitivity and recommend appropriate treatments. They can also provide professional cleaning and preventative care to maintain your oral health. Don’t hesitate to visit your dentist if you experience persistent or severe sensitivity or are worried about your oral health. Regular check-ups allow your dentist to identify problems early on.
Consult Your Dentist

If you experience persistent or severe sensitivity after teeth whitening, consult your dentist. They can determine the underlying cause of the sensitivity and provide a tailored treatment plan. The dentist will assess the condition of your teeth and gums. They might recommend a different whitening approach or suggest desensitizing treatments, like fluoride applications. Provide a detailed history of your symptoms, including when the sensitivity started, what triggers it, and how long it lasts. Following the dentist’s recommendations, you can get immediate relief and help to prevent further issues.
In-Office Treatments
Your dentist can offer in-office treatments to help reduce tooth sensitivity. These treatments might include the application of fluoride varnish, which strengthens the enamel. They may also recommend professional desensitizing agents or bonding agents to cover exposed dentin tubules. The in-office treatments provide a more concentrated dose of protective agents, offering quick relief. In some cases, your dentist may recommend dental procedures to address the underlying causes of the sensitivity, such as fillings for cavities or gum treatments for receding gums. Consulting with a dentist can give you some long-term relief.